Forms of Government: How Nations Are Ruled
Introduction — The Hook
Imagine living under a king who makes every law.
Or choosing your own leader through free elections.
Or being ruled by a single man with total power.
Every country in the world follows a system that decides who rules, how decisions are made, and how much freedom people have. This system is called a form of government.
Let’s explore the main forms of government that shape our world today:
Monarchy, Democratic, Dictatorship, Totalitarian/Authoritarian, Unitary, Federal, Confederation, Presidential, and Parliamentary.
1. Monarchy
A monarchy is a government ruled by a king or queen.
Power is inherited, usually passed down through royal families.
Key Features
- One ruler (king or queen)
- Rule by birthright
- Can be absolute or constitutional
Types and Examples
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Monarchy | The monarch has complete power. | Saudi Arabia |
| Constitutional Monarchy | The monarch shares power with a parliament or constitution. | United Kingdom, Japan |
Summary
- Monarchs are symbols of unity and tradition.
- Power can be limited or unlimited depending on the system.

2. Democratic Government
A democracy is a system where the people rule.
Citizens vote to elect leaders and shape laws.
Key Features
- Free and fair elections
- Equal rights for all citizens
- Government is accountable to the people
Main Types
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Democracy | People vote on every issue. | Switzerland |
| Representative Democracy | People elect leaders to make laws. | United States |
| Parliamentary Democracy | Prime Minister leads with parliament support. | United Kingdom |
| Presidential Democracy | President is elected separately from parliament. | USA, Brazil |
Summary
- Democracy gives citizens power and voice.
- It promotes equality, participation, and freedom.

3. Dictatorship
A dictatorship means one person controls everything.
People cannot question or oppose the ruler.
Key Features
- No free elections
- Power gained by force or manipulation
- Opposition is often punished
Examples
- Adolf Hitler in Nazi Germany
- Kim Jong-un in North Korea
Summary
- Citizens have no role in decision-making.
- Military or fear is used to keep control.

4. Totalitarian / Authoritarian Government
A totalitarian or authoritarian government controls every part of life — politics, media, and even thoughts.
Key Features
- No individual freedom
- Censorship and surveillance
- Controlled economy and media
Comparison Table
| Feature | Totalitarian | Authoritarian |
|---|---|---|
| Power Range | Controls all aspects of life | Controls political power only |
| Freedom | No freedom at all | Limited freedom |
| Example | North Korea | China |
Summary
- Power stays with a few leaders or one party.
- Citizens obey rather than participate.

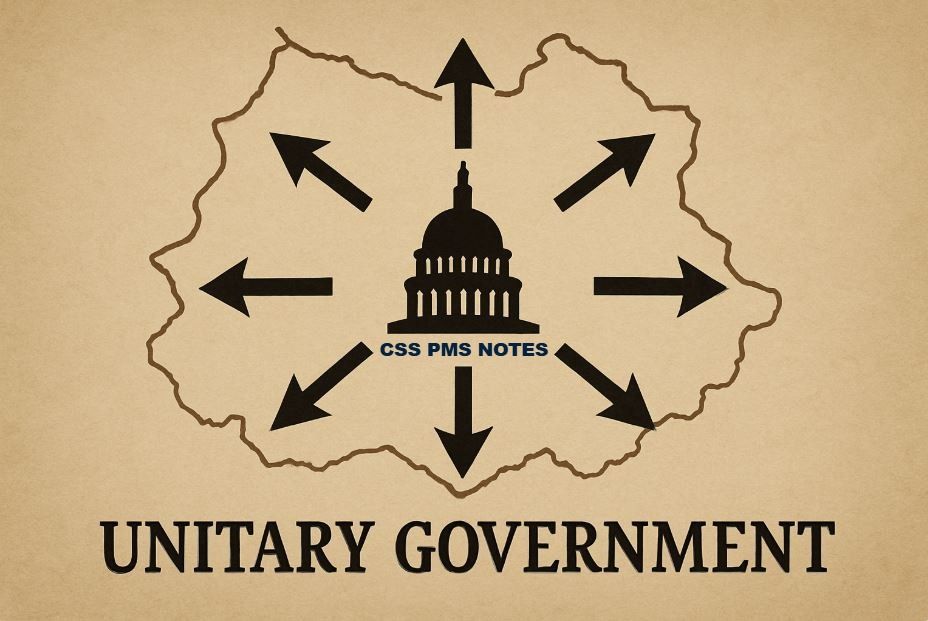
5. Unitary Government
A unitary government has a single central authority.
All decisions come from the national government, not local ones.
Key Features
- Centralized power
- Uniform laws for the whole country
- Local governments follow national policies
Examples
- France
- Japan
- United Kingdom
Summary
- Efficient and organized system.
- But sometimes local needs are ignored.
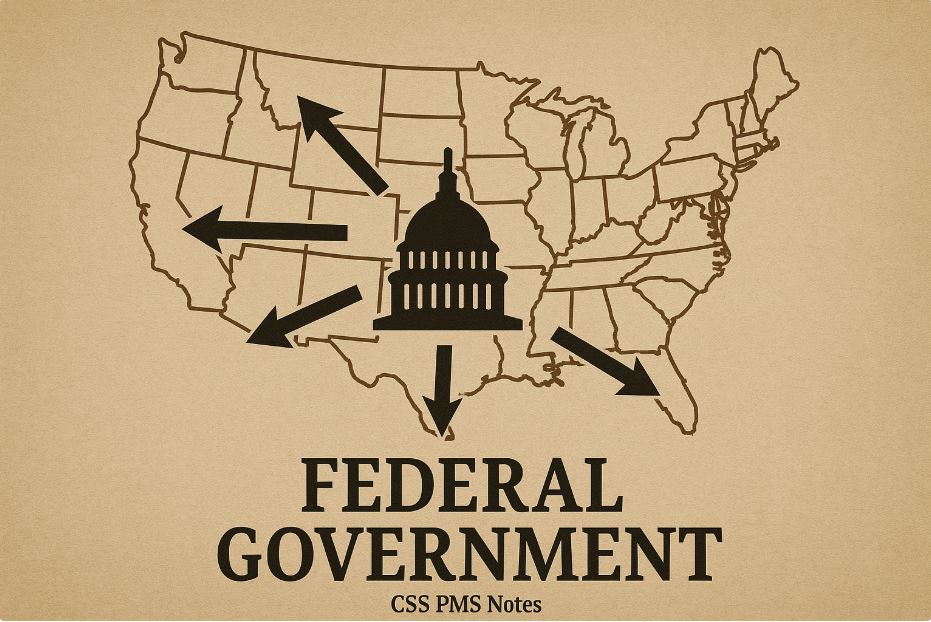
6. Federal Government
A federal government divides power between national and state levels.
Each level has its own authority.
Key Features
- Shared power between central and regional governments
- Constitution defines roles
- States can make local laws
Examples
- United States
- Pakistan
- Germany
Federal vs Unitary
| Feature | Federal | Unitary |
|---|---|---|
| Power Division | Shared | Centralized |
| Local Independence | Strong | Weak |
| Example | USA, Pakistan | France, Japan |
Summary
- Federal systems promote balance and flexibility.
- They allow local autonomy and national unity.
7. Confederation
A confederation is a union of independent states.
They work together for common goals but remain sovereign.
Key Features
- Weak central authority
- Member states control their own affairs
- Cooperation in defense or trade
Examples
- European Union (EU)
- Confederate States of America (historical)
Summary
- Best for alliances, not for strong central rule.
- Works well when countries want independence with cooperation.

8. Presidential Government
In a presidential government, the President is both the head of state and head of government.
The executive, legislative, and judicial branches are separate.
Key Features
- Fixed term for the president
- Clear separation of powers
- Direct election by the people
Examples
- United States
- Brazil
- Mexico
Advantages
- Strong and stable leadership
- Clear accountability
Disadvantages
- Possible conflict between branches
- Decision-making may be slow

9. Parliamentary Government
A parliamentary government links the executive and legislative branches.
The Prime Minister is the head of government, chosen by the majority party in parliament.
Key Features
- Prime Minister and cabinet from parliament
- Quick decision-making
- Government can fall through a no-confidence vote
Examples
- United Kingdom
- India
- Canada
Advantages
- Fast law-making
- Close coordination between branches
Disadvantages
- Frequent political changes
- Less separation of powers

Comparison of All Forms of Government
| Form | Who Rules | People’s Role | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monarchy | King/Queen | Limited | UK, Saudi Arabia |
| Democracy | People | Active | USA, India |
| Dictatorship | One ruler | None | North Korea |
| Authoritarian | Ruler or party | Very limited | China |
| Unitary | Central government | Moderate | France |
| Federal | Central + States | Shared | USA, Pakistan |
| Confederation | Independent states | Cooperative | EU |
| Presidential | Elected President | High | USA |
| Parliamentary | Prime Minister & Parliament | High | UK |
Conclusion
Forms of government define how power is used and how people live.
From monarchies ruled by kings to democracies powered by citizens, every system has its strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding these forms helps us value freedom, law, and good governance.
Whatever the system, the real purpose of government should always be — to serve the people and ensure justice.
FAQs
1. What are the main forms of government?
Monarchy, Democratic, Dictatorship, Totalitarian/Authoritarian, Unitary, Federal, Confederation, Presidential, and Parliamentary.
2. Which form of government gives most power to the people?
Democracy, because people choose their leaders through free elections.
3. What is the difference between Presidential and Parliamentary systems?
In a Presidential system, the President is separate from the legislature.
In a Parliamentary system, the Prime Minister is part of the parliament.
4. What is the oldest form of government?
Monarchy is the oldest and dates back to ancient times.
5. What type of government does Pakistan have?
Pakistan follows a Federal Parliamentary Democracy.