Bohr's Atomic Model
Introduction (Hook)
Atoms are very small particles, but they make everything in the universe. We cannot see atoms directly, so scientists developed atomic models to understand their structure. One of the most important and easy models is the
Bohr's Atomic Model
This model explains how electrons move around the nucleus in fixed paths and why atoms are stable.
What is Bohr's Atomic Model?
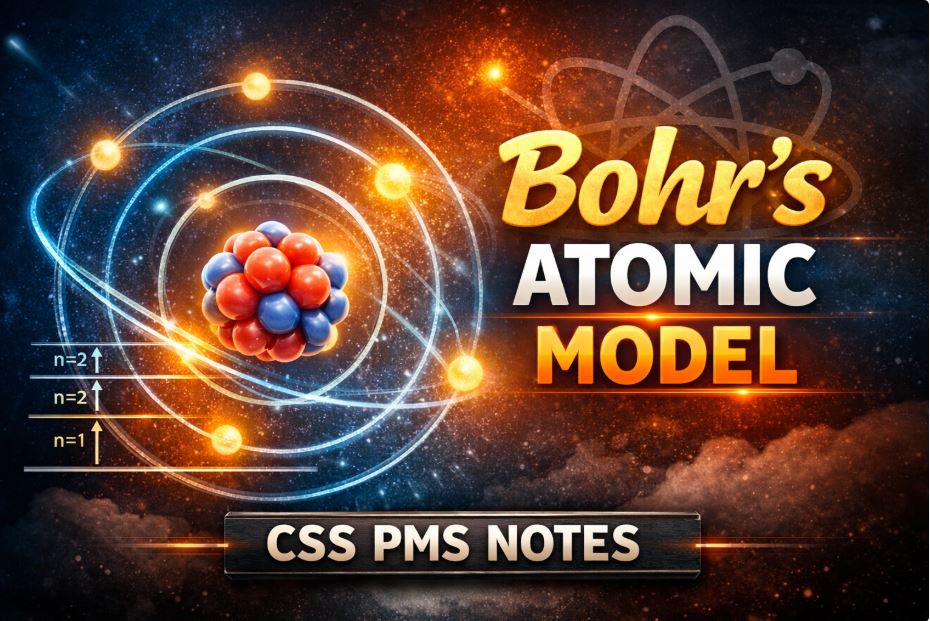
Niels Bohr proposed the Bohr Atomic Model in 1913. According to this model, electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed circular orbits called energy levels. Each energy level has a definite amount of energy, and electrons cannot exist between these levels. This model was mainly used to explain the structure and spectrum of the hydrogen atom.

Main Parts of Bohr's Atomic Model
1. Nucleus
- The nucleus is present at the center of the atom.
- It contains protons and neutrons.
- The nucleus contains nearly all of an atom’s mass.
2. Electrons
- Electrons are negatively charged particles.
- They move around the nucleus in fixed circular orbits.
3. Energy Levels (Orbits)
- Each orbit has fixed energy.
- Energy levels are represented as K, L, M, N or n = 1, 2, 3, 4.
- The energy of electrons increases as they move farther from the nucleus.

Postulates of Bohr's Atomic Model
Bohr proposed the following postulates:
- Electrons move in fixed circles around the nucleus.
- Each orbit has a fixed energy known as energy level.
- Electrons do not radiate energy while moving in a stable orbit.
- Energy is absorbed or emitted only when an electron jumps from one orbit to another.
- An electron absorbs energy when it jumps to a higher energy level.
- Energy is released in the form of light when an electron moves to a lower energy level.
Energy of Orbits in Bohr's Atomic Model
The energy of an electron in a particular orbit is given by the formula:
Eₙ = −13.6 / n² eV
Where n is the principal quantum number.
- Smaller value of n means lower energy.
- Larger value of n means higher energy.
Bohr's Atomic Model of Hydrogen Atom
The Bohr's Atomic Model successfully explains the hydrogen atom:
- Hydrogen has only one electron.
- The electron moves in fixed energy levels.
- When the electron jumps between energy levels, it produces spectral lines.
This explanation matched experimental results, which made the model very popular.
Advantages of Bohr's Atomic Model
- It explains the stability of atoms.
- It explains the hydrogen emission spectrum.
- It introduced the concept of energy levels.
- It is easy for students to understand.
Limitations of Bohr's Atomic Model
- It works only for hydrogen and hydrogen-like atoms.
- It fails for multi-electron atoms.
- It does not explain the small details in spectral lines.
- It contradicts Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle.
Importance of Bohr's Atomic Model
The Bohr's Atomic Model was a major step in the development of modern atomic theory. It helped scientists move from classical physics to quantum physics and laid the foundation for advanced atomic models.
Short Questions
- Who proposed the Bohr's Atomic Model?
- In which year was the Bohr's Atomic Model introduced?
- What are energy levels?
- Which atom is best explained by Bohr's model?
- What happens when an electron jumps to a higher orbit?
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- Bohr's Atomic Model was proposed in:
- A) 1905
- B) 1911
- C) 1913 ✅
- D) 1920
- The energy of an electron depends on:
- A) Shape of orbit
- B) Size of nucleus
- C) Principal quantum number ✅
- D) Charge of electron
- Bohr's model is applicable to:
- A) All atoms
- B) Multi-electron atoms
- C) Hydrogen atom only ✅
- D) Molecules
- Energy is released when an electron:
- A) Moves to higher orbit
- B) Moves to lower orbit ✅
- C) Stays in same orbit
- D) Leaves atom
Numericals Based on Bohr's Atomic Model
Numerical 1:
Calculate the energy of an electron in the second orbit of hydrogen atom.
Given: n = 2E₂ = −13.6 / (2)² = −13.6 / 4 = −3.4 eV
Solution :

Numerical 2:
Calculate the energy of an electron in the third orbit.
Given: n = 3E₃ = −13.6 / 9 = −1.51 eV
Solution

Conclusion
The Bohr's Atomic Model is one of the most important models in physics. Although it has limitations, it clearly explains the hydrogen atom and introduced the concept of fixed energy levels. Due to its simplicity and educational value, it is still taught in schools, colleges, and competitive exams like CSS and PMS.
CSS PMS Notes – Free education for everyone